What is an air source heat pump?
It is a type of heat pump that uses the air outside and converts the energy to provide your homes heating and hot water demands efficiently, comfortably while using a renewable technology.
What makes it a renewable energy source?
Well to answer this we first need to understand what renewable energy means!
In basic terms it is energy that comes from a source that’s won’t ever run out. It comes naturally from our environment such a wind power, solar power and hydroelectric, the fact that the air is its main fuel source makes Air Source HeatPumps an excellent low carbon solution using a renewable source to contribute towards heat demands.
What is its fuel source?
A some electricity(25%)Low Carbon Solution
Lots of outside air (75%)Renewable
How is it efficient compared to fossil fuels?
An air source heat pump can be more then 300-400% efficient dependent on the manufacture than an OIL, LPG,Gas & Coal boilers.
This is achieved by the heat pump producing more heating out then the energy that’s is put in.
How does it work?
Heat naturally moves from warmer places to colder places. Typically, in winter, outdoor air is colder than indoor air. But how can a heat pump provide heat from outdoors when the air outdoors is colder? To understand this, let’s look at the most common type of heat pump in the air-source solutions.
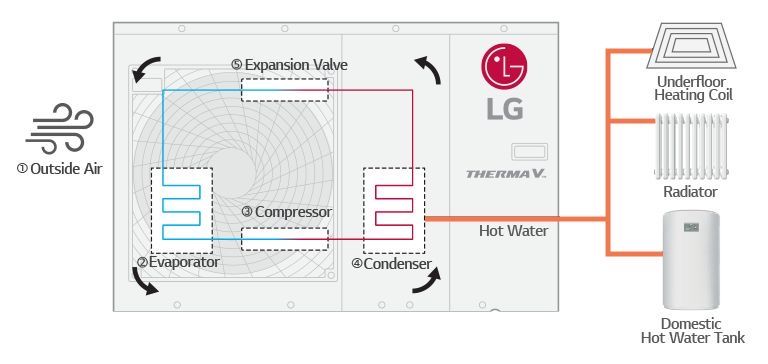
First of all, we need a refrigerant through which the heat will travel throughout the system. Heat from the outdoor air is absorbed into the evaporator and transferred to the refrigerant, even when it is cold outside. This is because even when outdoor temperatures are cold, there is still a good amount of energy that can be extracted from the air to be delivered into a building. For example, the heat content of air at -18°C equates to 85% of the heat contained at 21°C. Through this scientific process, the refrigerant receives heat from outdoor air and moves it into the house to provide heating and hot water. Then, the compressor in the heat pump uses electricity to compress the refrigerant and the temperature of the refrigerant increases. The compressed, high-temperature refrigerant becomes a gas and moves to the condenser, where heat from the gas refrigerant is transferred to water. When the heat is released in the condenser and expansion valve, the gas refrigerant cools and changes back into a liquid. As this process is repeated, the heat pump provides heating and hot water indoors. This process can also be reversed to remove heat for cooling in summer.
